Transforming the Way We Manage Data
Data is the backbone of today’s digital economy. With the ever-increasing volume of data being generated every day, the need for efficient, scalable, and robust data management solutions is more pressing than ever. Enter Kubernetes, the revolutionary open-source platform that’s changing the game of data management. Market research suggests that the demand for Kubernetes in data management is growing at a rapid pace, with a projected compound annual growth rate of over 30% by 2023.
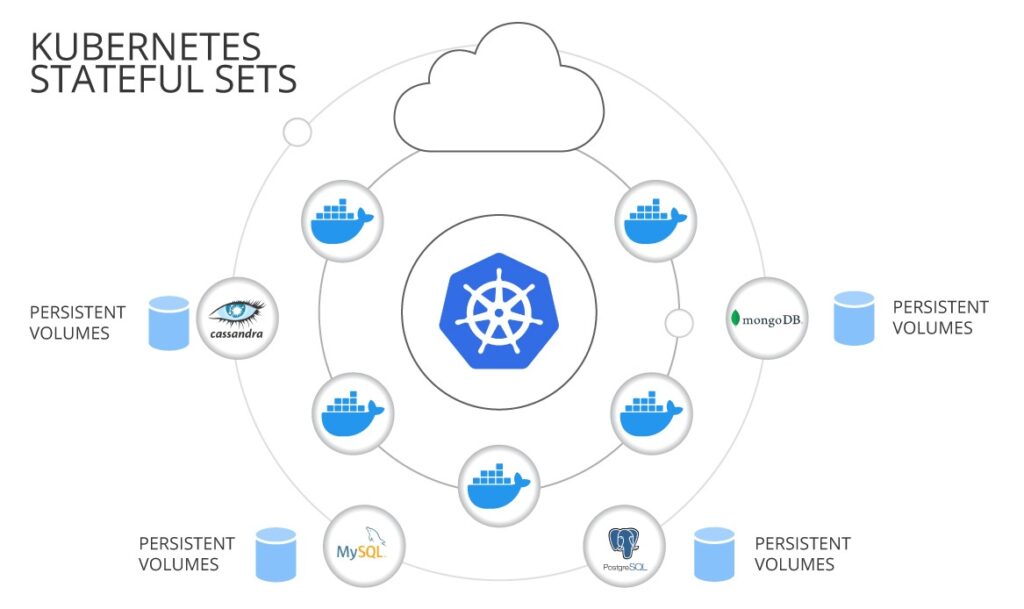
There is an increase in demand for Kubernetes. With its ability to automate deployment, scaling and management of containerized applications, is providing organisations with a new way to approach data management. By leveraging its container orchestration capabilities, Kubernetes is making it possible to handle complex data management tasks with ease and efficiency. Stateful applications, such as databases and data pipelines, are the backbone of any data management strategy. Traditionally, managing these applications has been a complex and time-consuming task. But with Kubernetes, stateful applications can be managed with ease, thanks to its Persistent Volumes and Persistent Volume Claims.
Data pipelines, the critical component of data management, are transforming the way organizations process, transform and store data. Kubernetes makes it possible to run data pipelines as containers, simplifying their deployment, scaling, and management. With Kubernetes in-built jobs support, these workflows can run as a scheduled or triggered jobs that are orchestrated by the Kubernetes engine. This enables organizations to ensure the reliability and efficiency of their data pipelines, even as the volume of data grows.

Scalability is a major challenge in data management, but with Kubernetes, it is by design. Its ability to horizontally scale the number of nodes in a cluster makes it possible to easily handle the growing volume of data. This ensures that data management solutions remain robust and scalable, even as data volumes increase.
Resilience in another key requirement in data management. Traditionally, a single point of failure can bring down the entire system. But with Kubernetes, failures are handled gracefully, with failed containers automatically rescheduled on healthy nodes. This provides peace of mind, knowing that data management solutions remain available even in the event of failures.
Kubernetes also offers zero downtime deployment in the form of rolling updates. This also applies to databases where the administrator can upgrade the database version without any impact to the service by rolling the update to one workload at a time until all replicas are upgraded.
To complement the resilience features, operations such as memory or CPU upgrades which, in the past, were considered destructive changes that required planning and careful change and release management. Today, since Kubernetes relies on declarative management of its objects, this change is just a single line of code. This change can be deployed similar to any code change that progresses to the different environments using CI/CD pipelines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Kubernetes is transforming data management. Gone are the days of regarding Kubernetes as a platform suitable only for stateless workloads leaving databases running on traditional VMs. Many initiatives took place to adapt stateful workloads to run efficiently and reliably in Kubernetes from releasing the StatefulSets API and Storage CSI, to building Kubernetes operators that will ensure databases can run securely in the cluster with massive resilience and scalability. With these operators being released for common database systems such as Postgres and mySQL to name a few, daunting database operations such as automatic backups, rolling updates, high availability and failover are simplified and taken care of in the background transparent to the end user.
Today, with more database vendors either releasing or endorsing Kubernetes operators for their database systems, and enterprises running databases in Kubernetes production environments successfully, there is no reason to think that it lacks the necessary features to run production enterprise database systems. The future of data management is looking bright, and we excitedly await what lies ahead thanks to the Kubernetes community’s constant drive for innovation and the expansion of the possibilities.
To learn more about Kubernetes and our service offering here.